PHP Superglobal Variables
The scope of the superglobal variables is everywhere. List of variables in a particular super global variables depends on the state of the PHP application.
PHP have Predefined “Super Global” variables for some specific purpose. Below list shows PHP superglobal variables-
- $GLOBALS
- $_SERVER
- $_REQUEST
- $_POST
- $_GET
- $_FILES
- $_ENV
- $_COOKIE
- $_SESSION
PHP $GLOBALS superglobal Variable
PHP $GLOBALS Variable is used to access the variable from anywhere in the PHP Script. You have to use the GLOBALS keyword before the variable.
Example -1 PHP $GLOBALS Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$x = 10;
$y = 20;
function multiplication()
{
$GLOBALS['z'] = $GLOBALS['x'] + $GLOBALS['y'];
}
multiplication();
echo "The multiplication is " . $z;
?>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, we have 2 local variables and we use these variable inside a function by using “GLOBALS” keyword.

PHP $_SERVER Super Global Variables
PHP $_SERVER Superglobal Variable which contains information about the header, paths, script location etc. and these pieces of information are collecting from the web server.
Example – 2 PHP $_SERVER Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];
echo "<br>";
echo $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'];
echo "<br>";
echo $_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME'];
echo "<br>";
echo $_SERVER['SCRIPT_FILENAME'];
?>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, we use $_SERVER variable to know the information about the server.

Others Parameters of $_SERVER Superglobal Variable
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’] | Replay with the filename of the currently executing script |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_ADDR’] | Replay with the IP address of the host server. |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_NAME’] | Replay with the name of the host server. | $_SERVER[‘SERVER_SOFTWARE’] | Replay with the server identification string. |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_PROTOCOL’] | Replay with the name and revision of the information protocol. | $_SERVER[‘GATEWAY_INTERFACE’] | Replay with the version of the Common Gateway Interface (CGI) the server is using |
| $_SERVER[‘REQUEST_METHOD’] | Replay with the request method used to access the page (such as POST). |
| $_SERVER[‘REQUEST_TIME’] | Replay with the timestamp of the start of the request. |
| $_SERVER[‘QUERY_STRING’] | Replay with the query string if the page is accessed via a query string | $_SERVER[‘HTTP_ACCEPT’] | Replay with the Received header from the current request. |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_ACCEPT_CHARSET’] | Replay with the Received Charset header from the current request. |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_HOST’] | Replay with the Host header from the current request. |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTPS’] | To know the request type it is https request or http request where https means secured request. |
| $_SERVER[‘HTTP_REFERER’] | Replay with the complete URL of the page through which the current page was called. |
| $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_ADDR’] | Returns the IP address of the client or visitor computer. |
| $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_HOST’] | Returns the name of HOST . |
| $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_PORT’] | Return the Port number of the communicating request port from the client computer. |
| $_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_FILENAME’] | Replay with the absolute pathname of the currently executing script. |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_ADMIN’] | Return the e-mail of the administrator of the web server. |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_PORT’] | Return the port number of the communicating request port from the server. |
| $_SERVER[‘SERVER_SIGNATURE’] | Returns the server-version and virtual host name. |
| $_SERVER[‘PATH_TRANSLATED’] | Returns the path of the file based systems. |
| $_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_NAME’] | Replay with the path of the current running script. |
| $_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_URI’] | Returns the URI of the script. |
PHP $_GET Superglobal Variable
All the information or parameter submitted from a form are stored in the $_GET Superglobal Variable if the method of the form is “get”.
Example – 3 PHP $_GET Example
<!-- Login Page --> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <form method="get" action="processlogin.php"> First name:<br> <input type="text" name="firstname"><br /> Last name:<br> <input type="text" name="lastname"><br /><br/> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </body> </body> </html>
<!-- Process(processlogin.php) page -->
<?php
print_r ($_GET);
echo "<br />";
$firstname = $_GET['firstname'];
$lastname = $GET['lastname'];
if (empty($firstname)) {
echo "Name is empty";
} else {
echo $firstname . " " . $lastname;;
}
?>
In the above example, we use the $_GET variable to collect the information from the form. When the user submits the page after clicking on the submit button this $_GET variable collect the values from the input field.
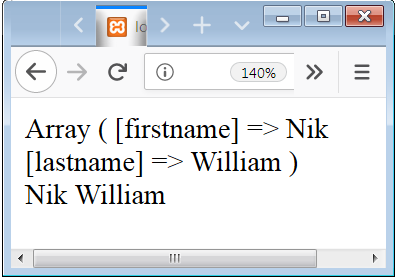
PHP $_POST Super Global
All the information or parameter submitted from a form are stored in the $_POST Superglobal Variable if the method of the form is “post”.
Example – 4 PHP $_POST Example
<!-- Login Page --> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <form method="post" action="processlogin.php"> First name:<br> <input type="text" name="firstname"><br /> Last name:<br> <input type="text" name="lastname"><br /><br/> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </body> </body> </html>
<!-- Process(processlogin.php) page -->
<?php
print_r ($_POST);
echo "<br />";
$firstname = $_POST['firstname'];
$lastname = $_POST['lastname'];
if (empty($firstname)) {
echo "Name is empty";
} else {
echo $firstname . " " . $lastname;;
}
?>
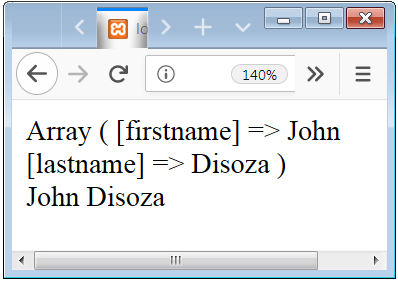
PHP $_REQUEST
All the information or parameter submitted from a form are stored in the $_REQUEST Superglobal Variable if the method of the form is “get” or “post”.
Example – 5 PHP $_REQUEST Example
<!-- Login Page --> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <form method="post" action="processlogin.php"> First name:<br> <input type="text" name="firstname"><br /> Last name:<br> <input type="text" name="lastname"><br /><br/> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </body> </body> </html>
<!-- Process(processlogin.php) page -->
<?php
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
// collect value of input field
print_r ($_REQUEST);
$firstname = $_REQUEST['firstname'];
$lastname = $_REQUEST['lastname'];
if (empty($firstname)) {
echo "Name is empty";
} else {
echo $firstname . " " . $lastname;;
}
}
?>
In the above example, we use the $_REQUEST variable to collect the information from the form. When the user submits the page after clicking on the submit button this $_REQUEST variable collect the values from the input field.

 June 11th, 2019
June 11th, 2019  Nilesh Chaurasia
Nilesh Chaurasia  Posted in
Posted in  Tags:
Tags: 

